📕Real Number Representation
- 프로그래밍 언어는 실수라고 부르는 fractions을 지원한다.
- 3.14159265(pi)
- 2.71828..(e)
- 등등등
- 명시적 표기법은 소수점 왼쪽의 한 자릿수가 있다.
- normalized number : 점 앞에 하나의 숫자가 와야 함.
- ex
- 1.0 * 10 ^ -9 -> Normalized,
- 10.0 * 10^-10 or 0.1 * 10^-8 -> Not normalized
- 이진수의 명시적 표시
- 1.0 * 2^-1
📕Floating Point
- Floating point는 숫자의 base에 따라 표현하는 숫자의 방식이 다르고, point의 위치도 달라지기에 floating point라고 부른다.
- 2진수의 형태

- 실수를 normalized form으로 표현하는 표준화된 방식은 3가지 이점을 가져온다.
- floating-point를 포함하는 데이터의 교환을 쉽게 해 준다.
- floating-point로 표현하는 숫자를 알기 쉽게 해 준다.
- word에 저장되는 숫자들의 정확성을 증가시킨다.
- binary point 오른쪽에 있는 숫자는 불필요한 0을 대체한다.
📕Floating-point Representation
- Floating-point number는 word에 일치해야 한다.
- fraction과 exponent에 크기 합의점을 찾아내야 한다.
- 교환은 precison과 range 사이에서 일어난다.
- fraction size를 증가시키면 -> fraction의 정확성이 증가한다.
- exponent size를 증가시키면 -> 숫자의 범위가 증가한다.
- RISC -V에서 floating-point를 표현하는 방법
- s : 1bit sign -> 0 : positive, 1 : negative
- 8 bit exponenet field (sign bit를 포함한다. 지수도 +,-가 있기 때문)
- 23 bits fracion field

- 일반적으로 floating point number are of the form

📕Over flow and Underflow
- floating-point는 엄~~~~~~~~~~~청 넓은 범위를 제공한다.
- 2.0 * 10^-38 ~ 2.0 * 10^38 -> 무한한 범위는 아님.
- floating-point에서도 정수와 같이 overflow가 일어난다.
- 만약 0이 아닌 fraction이 엄~~~ 청 작다면 그것은 표현할 수 없을까?
- 새로운 개념이 등장 -> underflow
- floating-point에서 오버플로우와 언더플로우
- 오버플로우는 exponent 가 엄청 클 때
- 언더플로우는 부호가 음수인 exponent가 엄청 클 때
- 언더플로우와 오버플로우를 줄이기 위한 방법? 노력?
- 64-bit double precision floating-point format
- Number range is 2.0 * 10^-308 ~ 2.0 * 10^308 in decimal
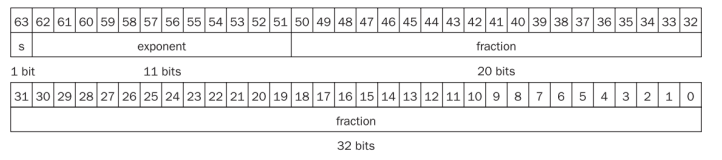
📕IEEE 754 Floating-Point Standard
- Floating-Point 표준화는 1985년에 이뤄짐.
- 두 가지 표현방식이 있음.
- 32-bit single precison
- 64-bit double precison


- S : sign bit (0: non-negative, 1: negative)
- Normalized significand : 1 + F(1.0 <= Significand < 2.0)
- hidden bit를 가진다. [ leading pre-binary-point 1bit]
- Significand는 1+F이다. ex) F : 1010 -> Significand : 1.1010
- 24 bits in single precison (23-bit fraction + 1 (1bit))
- Minimum when F= 00000000~ -> Significand : 1.0
- Maxinum when F= 1111111111~ -> Significand : 1.11111111111111~
- Exponent : Actual exponent + Bias = Biased exponent
- Ensure exponent is unsigned (Actual : -126 ~ 127 -> Biased : 1 ~254)
- Biases are 127 and 1023 in single and double precision
📕Biased Exponent
- IEEE 754 설계자들은 정수를 비교하듯이(e.g., sorting) floating-point 표현방식도 그렇게 쉽게 진행되기를 원했다.
- Sign-bit는 MSB에 있고, 그것을 비교해서 빠른 비교가 가능하다.
- Significand 전에 exponent를 위치해있기에, 두 floating-point를 비교하는데 용이하다.
- 음의 지수는 비교를 하는데 문제를 일으킨다 -> Biased exponent 도입.
💡Actual exponent representation
X= 1.0 * 2^-1
011111111000000~
Y=1.0* 2^1
00000001000000~
이렇게 Actual exponent를 사용하게 되면 X가 Y보다 실제로는 작지만 표기법상 큰 수로 표현된다.
따라서 Biased exponent를 도입해서 비교의 혼동을 막았다.
💡Biased exponent representation
- single precison인 경우 exponent + 127
- double precison인 경우 exponent+ 1023
X=1.0 * 2^-1 (-1 + 127) => 01111110
00111111000000
Y=1.0 * 2^1 ( 1 + 127) => 10000000
0100000000000
📕IEEE 754 Encoding
- IEEE 754 encoding of floating-point numbers
- 특별한 상황을 표현하기 위해 특별한 symbols가 있다.
- NAN -> invaild operations, such as 0/0

- Single precision range is
- 최솟값 : ∓1.0 * 2 ^(-126) => 1.2 * 10 ^(-38)
- E : 00000001 (actual exponent : 1-127 = -126 ), F : 0000000 ~ (Significand : 1.0)
- 최댓값 : ∓(2.0 -⋴) * 2^(127) -> 3.4 * 10^(38)
- E : 11111110 (actual exponent 254-127 =127), F : 111111111~ (Significand : 2.0-⋴)
- E : 0000 0000 and 1111 1111?
- 최솟값 : ∓1.0 * 2 ^(-126) => 1.2 * 10 ^(-38)
📕IEEE 754 Representation Example
- -0.75를 표현해라
- -0.75
- = -3/4 or -3/2^2
- = -11(2)/2^2 or -0.11(2)
- = -0.11 (2) * 2 ^ (0)
- -1.1(2) * 2^(-1)
- 1 0111 1110 10000~
- 빨 : sign-bit = 1
- 파 : exponent = -1 + 127 => 126 (0111 1110)
- 노 : fraction = 10000000 -> 1
- -1+(F). 2^(exponent - 127) = -1.1 * 2^(-1)
- -0.75
📕10진수에서 floating-point 덧셈
- floating-point에서 2개의 10진수를 더할 때
- 9.999* 10 ^(1) + 1.610 * 10^(-1)
- 가정 : 2 digit exponent & 4 digit Significand
- 더하는 과정
- 작은 쪽의 exponent를 큰 쪽의 exponent로 변경함.
- 9.999 * 10 ^ 1 + 0.016 * 10 ^ 1
- 유효숫자를 더함.
- 9.999 + 0.016 = 10.015
- Normalize 하고 오버플로우와 언더플로우를 check 함.
- 1.0015 * 10^2
- Round the sum
- 왜냐하면 유효숫자에 bit가 4bit라고 가정했는데 현재 5bit를 사용하기에 반올림을 해서 4bit로 만들어준다.
- 1.002 * 10^2
- 만약 round를 했는데 Normalize 되지 않았다면 다시 Normalize 해준다.
- ex) 9.999 * 10 ^2 -> 10.000 * 10^2 -> 1.000 * 10^3
- 작은 쪽의 exponent를 큰 쪽의 exponent로 변경함.
- 더하는 과정
📕2진수에서 floating-point 더하기
- floating-point에서 두 개의 이진수 더하기.
- 0.5 + (-0.4375)
- 0.5= 1* 1/2 = 1* 2^-1 = 1.000 * 2^ -1
- -0.4375 = -7 * 1/16 = -111 * 2^(-4) = -1.110 * 2^(-2)
- 0.5 + (-0.4375)
- 더하는 과정
- 작은 쪽의 exponent를 큰 쪽의 exponent로 맞춤.
- -1.110 * 2^(-2) = -0.111 * 2^(-1)
- 유효 숫자 더하기
- 1.000 + (-0.111) = 0.001
- Normalize & 오버플로우, 언더플로우 검사
- 0.001 * 2^ (-1) = 1.000 * 2^(-4) -> exponent 검사.
- Round the sum
- 1.000* 2^(-4) -> 라운드 할 필요 없음.
- 1.000 * 2^(-4) -> 1/16 = 0.0625
- 작은 쪽의 exponent를 큰 쪽의 exponent로 맞춤.
📕10진수 floating-point 곱하기
- 10진수 두 개 곱하기
- 1.110 * 10 ^(10) * 9.200 * 10^(-5)
- 가정 : exponent 2bit, Significand 4bit
- 곱하기 과정
- exponent는 서로 더한다.
- new exponent : 10 + -5 = 5
- Biased exponent : (10+127) + ( -5 + 127) = 259 (X)
- (10+127) + ( -5 + 127) - 127 = 132 = (5+127) (O)
- 유효 숫자 곱하기
- 1.110 * 9.200 = 10.212000 = 10.212 * 10 ^5
- 정규화 & 오버플로우, 언더플로우 체크
- 1.0212 * 10 ^ 6
- Round the sum
- 1.021 * 10 ^ 6
- Sign-bit 결정하기
- + 1.021 * 10 ^ 6
- exponent는 서로 더한다.
📕2진수 multiplication in Floatin-Point
- 두 개의 이진수 곱하기
- 0.5 * (-0.4375) = 1.000 * 2^(-1) * -1.110 * 2^(-2)
- 곱하는 과정
- exponent 서로 더하기
- new exponent : -1 + (-2) = -3
- Biased exponent : (-1 + 127) + (-2 + 127) - 127 = -3+127
- 유효숫자 곱하기
- 1.000 * 1.110 = 1.110000 -> 1.110
- 정규화, 오버플로우, 언더플로우 체크
- 1.110 * 2^(-3)
- Round the sum
- 할 필요 x
- sign 결정하기
- -1.110 * 2^(-3)
- -1.110 * 2^(-3) = -0.001110 = -7/2^5 = -7/32 = -0.21875
- exponent 서로 더하기
📕Floating-Point Instructions in RISC - V
| instruction(.s : single , .d : double) | Description |
| fadd.s / fadd.d , fsub.s/ fsub.d | floating-point addition, subtraction |
| fmul.s/ fmul.d , fdiv.s/fdiv.d / fsqrt.s/fsqrt.d | floating-point multiplication, divison, square root |
| feq.s / feq.d, flt.s/flt.d , fle.s/fle.d | floating-point equals, less-than, less-than-or-equal |
📕Accurate Arithmetic
- 정수와 다르게 floating-point 숫자들은 근사치로 표현된다. [ 실제로는 표현할 수 없다]
- 따라서 우리는 floating-point 표현을 실제 수와 가깝게 만들 필요성이 있다.
- IEEE 754는 rounding 하는데 몇 가지 모드를 제공한다.
- IEEE 754는 가드 및 라운드라고 하는 항상 오른쪽에 두 개의 추가 비트를 유지합니다.
- ex) 2.56 * 10 ^ 0 + 2.34 * 10 ^2
- 작은 쪽의 지수를 큰 쪽을 맞출 때 point 앞에 뒤에 있던 숫자 중 앞에서 1번째와 2번째를 각 guard, round라고 부름.
- 2.56 * 10 ^ 0 -> 0.0256 * 10 ^2 (5: guard digit , 6 : round digit)
2.34 2.3400
+ 0.02 -> 2.36 * 10^2 + 0.0256 -> 2.37 * 10^2
= 2.36 = 2.3656
가드와 라운드가 없는 경우 가드와 라운드가 있는 경우
더 정확한 숫자를 표현할 수 있다.~!@~!@
📕IEEE 754 Rounding
- IEEE 754은 4개의 rounding mode를 지원한다.
- default mode는 round to nearest even

- Round toward zero
- 0과 가까운 반올림
- Round toward Positve Infinity
- 양의 무한대 방향으로 반올림
- Round toward Negative Infinity
- 음의 무한대 방향으로 반올림
- Round to Nearest Even(default)
- 가까운 방향으로 반올림
- ex) -2.75는 -3과 -2중에서 -3과 가깝다. 따라서 -3으로 반올림됨.
- 그럼 만약 정중앙에 있다면?
- 짝수로 반올림한다.
- ex) 2.5 => 2, 3.5=> 4
- 짝수로 반올림한다.
- 가까운 방향으로 반올림
📕Ground, Round, and Sticky Bits
- IEEE 754는 halfway case를 다루기 위해서 guard, round, sticky (GRS) bits를 뒀다.
- Guard : bit immediately after LSB of fraction
- Round : bit to the right of the guard bit
- Sticky : logical OR of all other bits after guard and round bits
💡1.0101001000010 * 2^4
- 파란 부분에서 첫 글자는 Guard
- 두 번째 글자는 Round
- 첫 글자와 두 번째 글자를 제외한 영역에서 or 처리해서 1이 하나라도 있다면 Sticky는 1, 그 외의 경우에는 0
📕Round to nearest even with GRS in IEEE 754
- if GRS is 000~ 011 -> round down (leave fraction)
- if GRS is 101~ 111 -> round up ( fraction +1)
- if GRS us 100 (halfway) -> fraction에 LSB를 보고 판단함.
- if LSB is 0 -> 반올림 X 1.010100100* 2^4 -> 1.010100 * 2^4
- if LSB is 1 -> 반올림 O 1.010101100 * 2^4 -> 1.010110 * 2^ 4
'Computer Science > Computer Architecture' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Computer Architecture] - processor (2) (0) | 2022.11.12 |
|---|---|
| [Computer Architecture] - processor (1) (0) | 2022.10.23 |
| [computer archiecture] - arithmetic_for_computers(1) (0) | 2022.10.19 |
| [computer architecture]-instruction_language_of_computer(3) (0) | 2022.10.11 |
| [computer architecture]-instructions_language_of_computer(2) (0) | 2022.10.09 |
